Work-related injuries are a significant concern for both employees and employers. In the realm of orthopedics, these injuries can range from acute traumas to chronic conditions caused by repetitive stress and strain. Understanding the common types of work-related orthopedic injuries is essential for prevention, management, and ensuring workplace safety. Here, we delve into the most prevalent types of work-related injuries that orthopedic specialists frequently encounter.
1. Repetitive Strain Injuries (RSIs)
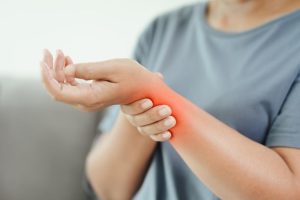
Description: RSIs are caused by repetitive motions that stress the muscles, tendons, and nerves. They are common in jobs that require continuous hand or arm movements, such as typing, assembly line work, or using vibrating tools.
Common RSIs:
- Carpal Tunnel Syndrome: Compression of the median nerve in the wrist, causing pain, numbness, and tingling in the hand.
- Tendinitis: Inflammation of the tendons, particularly in the wrist, elbow, and shoulder.
Prevention and Management:
- Ergonomic adjustments
- Regular breaks
- Stretching exercises
- Anti-inflammatory medications
2. Lower Back Injuries
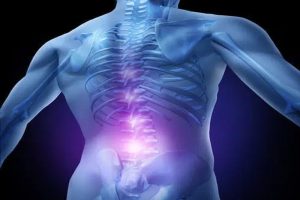
Description: Lower back injuries are among the most common orthopedic issues in the workplace. They can result from heavy lifting, improper posture, or prolonged sitting.
Common Lower Back Injuries:
- Herniated Discs: Displacement of the disc material in the spine, leading to pain and nerve compression.
- Muscle Strains: Overstretching or tearing of muscles in the lower back.
Prevention and Management:
- Proper lifting techniques
- Ergonomic chairs and workstations
- Core strengthening exercises
- Physical therapy
3. Shoulder Injuries
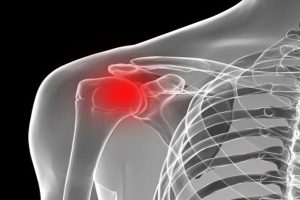
Description: Shoulder injuries can occur from repetitive overhead activities, heavy lifting, or trauma. These injuries are common in construction, manufacturing, and healthcare settings.
Common Shoulder Injuries:
- Rotator Cuff Tears: Tears in the muscles or tendons that stabilize the shoulder joint.
- Bursitis: Inflammation of the bursae, small fluid-filled sacs that cushion the shoulder joint.
Prevention and Management:
- Proper lifting techniques
- Avoiding repetitive overhead movements
- Strengthening shoulder muscles
- Anti-inflammatory treatments
4. Knee Injuries
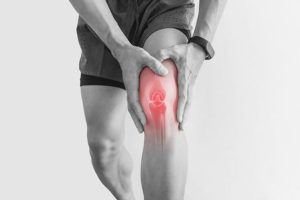
Description: Knee injuries often result from repetitive strain, heavy lifting, or sudden impacts. These are prevalent in occupations involving manual labor, prolonged standing, or frequent kneeling.
Common Knee Injuries:
- Meniscus Tears: Tears in the cartilage that cushions the knee joint.
- Patellar Tendinitis: Inflammation of the tendon connecting the kneecap to the shinbone.
Prevention and Management:
- Knee pads for protection
- Strengthening and flexibility exercises
- Weight management
- Physical therapy
5. Ankle and Foot Injuries
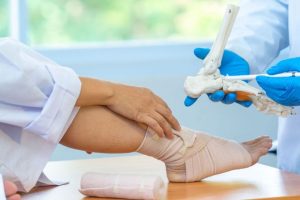
Description: These injuries are common in occupations that require prolonged standing, walking on uneven surfaces, or carrying heavy loads. Ankle sprains and plantar fasciitis are frequent concerns.
Common Ankle and Foot Injuries:
- Ankle Sprains: Stretching or tearing of the ligaments in the ankle.
- Plantar Fasciitis: Inflammation of the plantar fascia, the ligament connecting the heel to the toes.
Prevention and Management:
- Proper footwear
- Ankle braces or supports
- Stretching and strengthening exercises
- Anti-inflammatory treatments
6. Neck Injuries

Description: Neck injuries can be caused by poor posture, repetitive motions, or trauma. They are common in desk jobs, driving, and jobs requiring heavy lifting.
Common Neck Injuries:
- Cervical Strain: Overstretching or tearing of the muscles in the neck.
- Herniated Cervical Disc: Displacement of the disc material in the cervical spine.
Prevention and Management:
- Ergonomic adjustments
- Regular breaks to stretch and move
- Strengthening neck muscles
- Physical therapy
Conclusion
Work-related orthopedic injuries can significantly impact an individual’s quality of life and productivity. Employers and employees must prioritize workplace safety, adopt ergonomic practices, and seek early intervention for any signs of injury. Through a combination of preventive measures and effective treatment strategies, the risk of work-related orthopedic injuries can be minimized, ensuring a healthier and more productive workforce. If you experience any symptoms of these injuries, consulting an orthopedic specialist is crucial for proper diagnosis and treatment.
